Simple Example of using sp_execute_external_script with Python
04 Nov 2020Introduction
Since the release of Microsoft SQL Server 2017, Microsoft has introduced the ability to execute Python code direct from within the SQL Server environement. Now my first question was why? Well over time I came to the conclusion that SQL Server is not always the best/only tool for the job and thus this feature allows us to perform more complex and complete functions for example string distance functions in SQL Server. We perform many of these on a daily basis like JaroWinkler, which works great except that I can do it even quicker in Python as it is a RBAR operation.
You can read more on this at Docs
Code
Create Table for Demo
Lets start off by creating our input dataset, in most cases you would already have a dataset in mind for this. If that is the case you can skip the next 2 steps.
CREATE TABLE Employees
(
Id INT IDENTITY(1,1) PRIMARY KEY,
Firstname varchar(50),
Surname varchar(50),
EmailAddress varchar(50)
)
Insert Records into table
Insert some dummy data for processing.
INSERT INTO Employees VALUES ('JP','Voogt','jvoogt1@outlook.com')
INSERT INTO Employees VALUES ('John','Smith','john.smith@gmail.com')
INSERT INTO Employees VALUES ('Faf','De Klerk','faffie@webmail.com')
Python script
Note that I will pass my data(SQL Query) from SQL Server to Python using my_input_data, and OutputDataSet as my final output. You will need to know what columns and datatypes you will be expecting back from Python.
In this example we will use pandas to take the first letter of the Firstname and the Surname and combine them to create our OutputName column. This is just an easy example of how to perform string manipulation operations in Python
DECLARE @NewScript NVARCHAR(MAX)
SET @NewScript = N'
import pandas as pd
#Read Data From Input @input_data_1
df = my_input_data
#Perform String Manipulation
df["OutputName"] = df.apply(lambda x : x.Firstname[0] + " " + x.Surname, axis=1)
#Assign pandas.DataFrame to our spesified OutputDataSet
OutputDataSet = df
'
EXEC sp_execute_external_script
This is now where it all comes together, We indicate that we want to use Python, provide the input script, the input data and specify what the expected output will look like.
EXEC sp_execute_external_script
@language = N'Python'
, @Script = @NewScript
, @input_data_1 = N'SELECT * FROM Employees'
, @input_data_1_name = N'my_input_data'
WITH RESULT SETS ((Id int, Firstname varchar(50), Surname varchar(50), EmailAddress varchar(50), OutputName varchar(50)))
Results
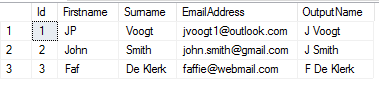
Conclusion
Disclaimer: Content is accurate at the time of publication, however updates and new additions happen frequently which could change the accuracy or relevance. Please keep this in mind when using my content as guidelines. Please always test in a testing or development environment, I do not accept any liability for damages caused by this content.
If you liked this post, you can share it with your followers or follow me on Twitter!